- Home
- Product Catalog
-
Product Introduction
- Isolation Gown
- Surgical Gown
- Cesarean Section Pack
- Baby Delivery Surgical Pack
- General Surgery Pack
- Angiography Surgery Pack
- Ophthalmic Drape Pack
- Dental Surgical Pack
- Neuro Surgical Pack
- Cardiovascular Surgical Pack
- Orthopedic Pack
- Radiology Pack
- Urology Surgical Pack
- ENT Surgical Pack
- Surgical Equipment Cover
- Accessories
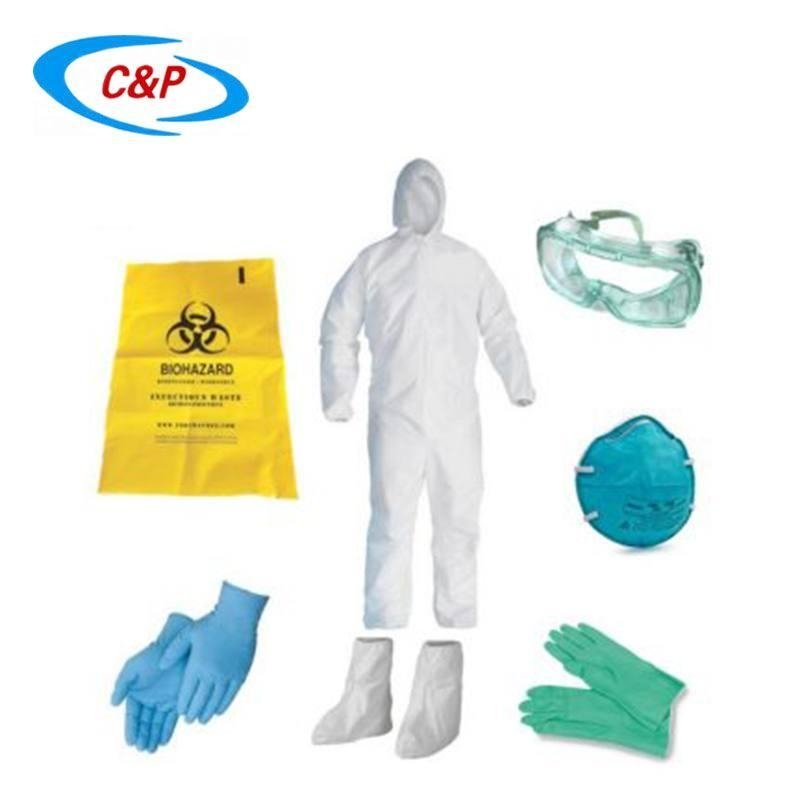
- Protective Products
- Face Mask
- Our Factory
- Contact Us
-
Blog
- Why do we use drapes in surgery?
- Why is non-woven fabric used to manufacture disposable items for hospital use?
- What are the 4 categories of surgery?
- What are the principles of draping?
- How do you drape a patient?
- Why use impervious stretchable stockinettes?
- How to remove surgical drapes?
- Why is the surgical pack so useful?
- Why use the TUR surgical drape?
- How to wear surgical gown
- What is an equipment cover?
- How to put on and take off personal protective equipment?
- Why use a caesarean section drape?
- What is the purpose of a patient surgical drape?
- When is a fenestrated drape used?
- What does a shoe cover do?
- How to wear and take off isolation gown?
- How to choose the right surgical drape?
- Why face mask is used?
- How to use disposable cesarean section surgery pack?
- What is an adhesive surgical drape?
- What is surgical gown used for?
- What is the difference between the four levels of isolation gown?
- How to use the angiography drape?
- Why is fluid collection pouch used during surgery?
- What is surgical gown?
- How do you drape eye surgery?
- How do you use a surgical gown?
- What is level 3 isolation gown?
- Why do doctors wear surgical gowns during surgery?
- Five steps to use the knee arthroscopy drape
- What is the under buttock drape?
- How to fold isolation gown?
- The application of AAMI medical surgical gowns at all levels
- What is a universal surgical pack?
- What is a fenestrated drape used for?
- How to use surgical gown?
- What is baby birth delivery drape pack?
- What is cesarean section surgery drape?
- Why is a fenestrated drape helpful during surgery?
- How to fold the surgical hole towel?
- How to fold surgical gown?
- What is extremity drape pack?
- How to wrap a surgical pack?
- When do you need to wear isolation gowns?
- What is SMS disposable surgical drape
- Why is the surgical gown green or blue?
- Can isolation gown be reused?
- Why face mask has expiry date?
- What is sms isolation gown?
- What is eye surgery drape?
- What is reinforced surgical gown?
- Why need a drape during surgery?
- What is surgical pack?
- What is AAMI level 2 isolation gown?
- Can surgical gowns prevent virus invasion?
- How to distinguish disposable isolation gown, protective gown and surgical gown
- What is an isolation gown used for
- The EN13795 standard was revised this year
- HS Code for some non-woven fabrics and their products
- What are fenestrated drape
- How to put on and take off the surgical gowns?
-
Product Videos
- Isolation Gown
- C-section Pack
- Surgical Gown
- Baby Birth Delivery Pack
- General Drape Pack
- Angiography Pack
- Knee Arthroscopy Pack
- Eye Surgical Pack
- Laparotomy Surgical Pack
- Orthopedic Surgery Pack
- Hip Drape Pack
- Dental Pack
- Cardiovascular Pack
- Cystoscopy Surgical Pack
- Oil resistance test
- How to wear isolation gown
- Production Process